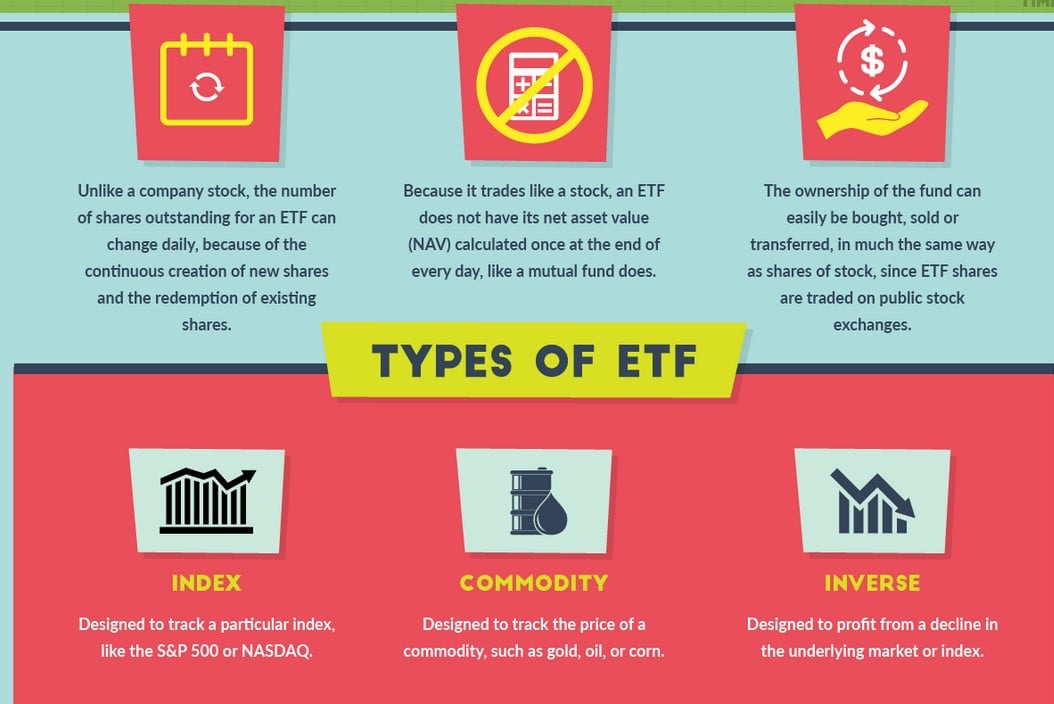
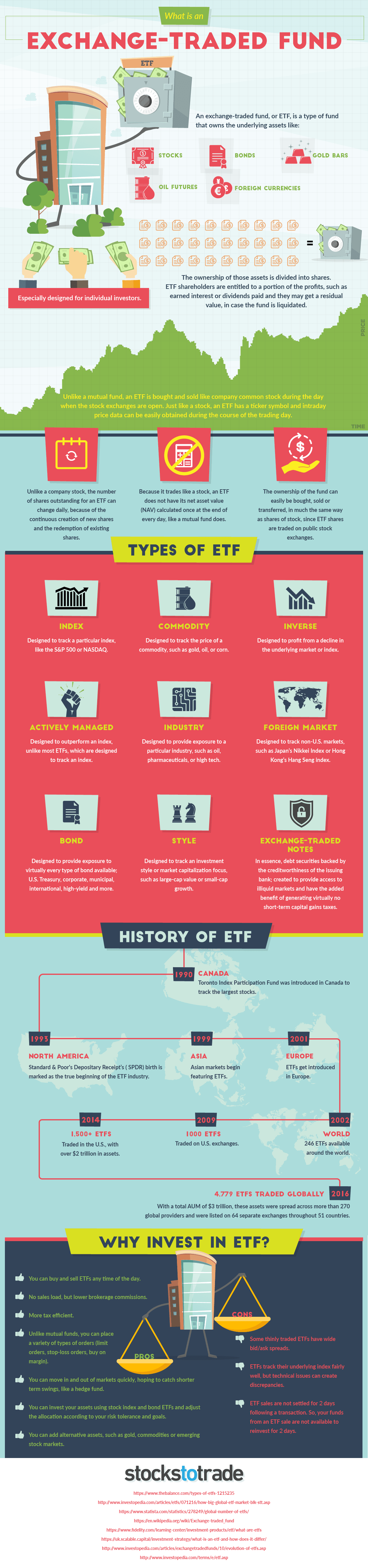
In 1989, the idea for the exchange-traded fund (ETF) was born.
Initially marketed to investors as Index Participation Shares, this innovative new product was meant to be a proxy for the S&P 500 that also traded on an exchange like a stock. After being launched, this early ETF prototype was immediately targeted by lawyers of the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) for illegally behaving like a futures contract. A lawsuit ensued, and a federal judge in Chicago ruled that they needed to be withdrawn.
A year later, the case can be made that Canada was the birthplace of the first successful ETF. This time the product was called Toronto 35 Index Participation Units (TIPs 35), and it tracked the TSE-35 Index at the time. TIPs were instantly lauded for providing low-cost exposure to Canadian equities – and shortly after, many more ETFs in Canada and the United States would follow suit, including the SPDR S&P 500 Trust ETF in 1993.
How do ETFs work?
Today’s infographic from StocksToTrade.com highlights the basics around ETFs, including how they work, what type of assets they can track, and the pros and cons associated with investing in them.
Article by Jeff Desjardins, Visual Capitalist