There’s a lot being done nowadays to reverse the effects of carbon emissions. It’s still not enough, but industries across the world are taking proactive measures to help reduce their negative impact on the environment. In construction, some buildings are now carbon neutral, meaning that the building has no net release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. We’re encouraged to buy locally sourced food products to cut down on carb emissions resulting from transportation of food. And we’ve definitely all come across the question, “Do you really need to print this email?”
It’s not just the physical things that cause carbon emissions however. We’re so used to our ever expanding digital lives being played out through a screen, that we don’t really think much about how this affects the environment. There is a price to pay though for our internet usage. For every tweet, comment, email and google search, a small amount of CO2 is emitted. It may not be a huge amount for one single person, but when you count up how many emails are being sent each day and how many social media users exist around the world, that amount suddenly becomes very big.
It’s estimated that by 2021, there will be 3.02 billion users of social media. That’s 41% of the world’s population. Facebook say that each of their users emits 299g of CO2 per year. Not bad. But for 3.02 billions users? It adds up and the number of users is expected to grow beyond 3.02 billion at 2021.
With more and more of our lives happening digitally, from shopping online for goods and services, to our jobs, banking and daily communication, we’re relying on technology to keep our world turning. Thanks to the colossal number of data centres that are now needed to feed planet earth’s internet obsession, the online world is now beginning to damage the real world.
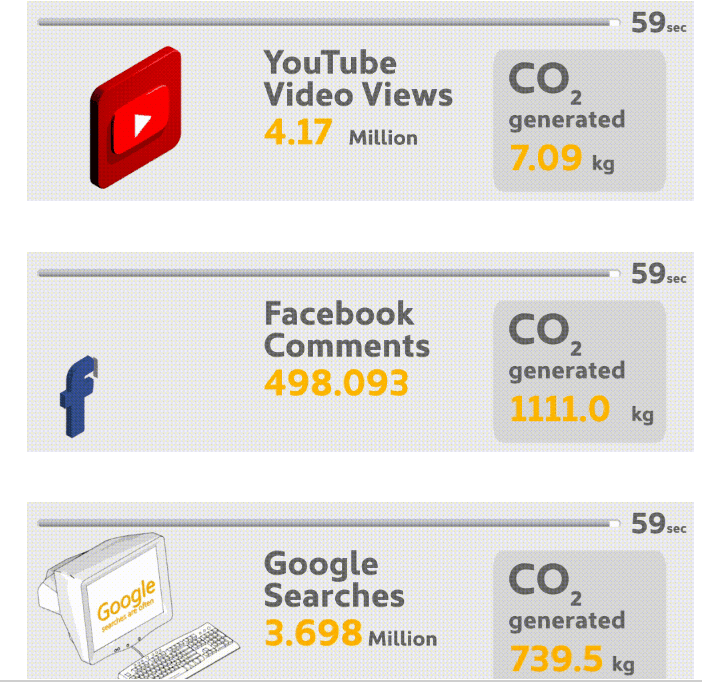
Credit Brokers Credit Angel looked into the carbon footprint of the internet and found out some shocking statistics. If you think the internet can’t possibly be producing that much CO2, think again. Let’s start with the world’s data centres. They’re stuffed from top to bottom with servers. Those servers are filled with web pages, apps, downloadable files and databases that we’re all so familiar with on a day to day basis. All this data runs on a lot of electricity, not just for powering the machines, but for providing air conditioning to keep the machines from overheating.
That’s just the beginning. PC’s and monitors are power hungry. When you total it all up, you can say that the internet burns around as much fossil fuel as is burned in Turkey or Poland in one year. For a closer look at the carbon footprint of the internet, check out this infographic from Credit Angel.
The Carbon Footprint Of The Internet
YouTube
Emails